Stroke
What is a Stroke?
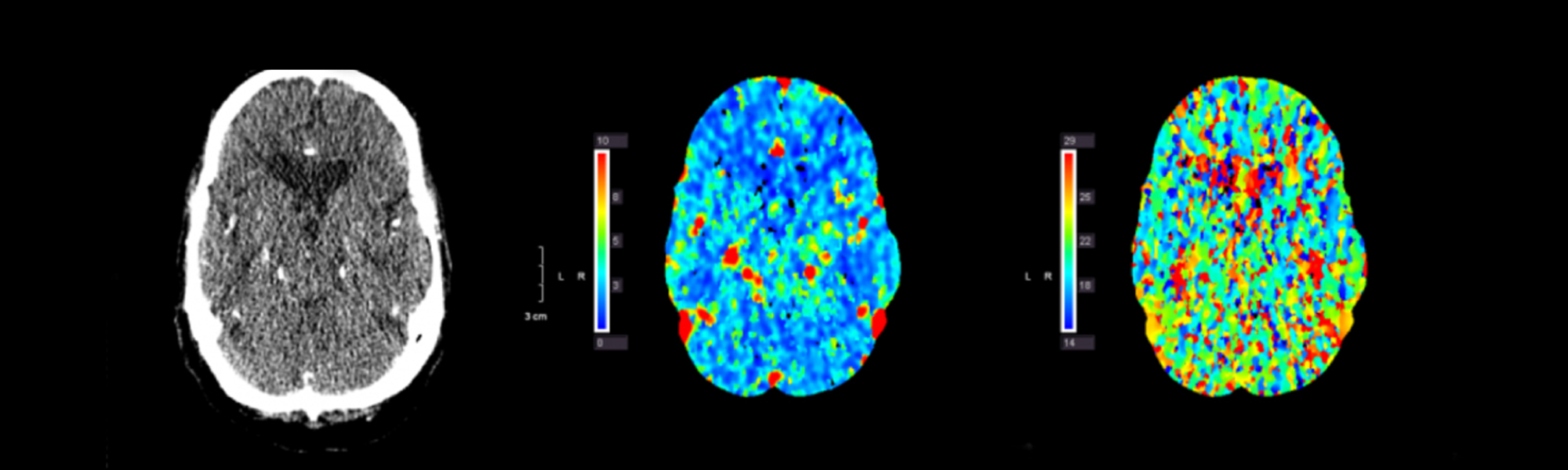
A stroke is a medical emergency that occurs when blood flow to the brain is disrupted, either by a blood clot or a ruptured blood vessel. As a result, brain cells are deprived of oxygen and nutrients, leading to damage and cell death.
A stroke, also called a “brain attack,” is caused when a blood vessel bringing blood and oxygen to the brain gets blocked or ruptures.
When this happens, brain cells do not get the blood that they need. Deprived of oxygen, nerve cells stop working and die within minutes. The effects of stroke can be permanent depending primarily on where it occurs in the brain, and how long it takes to be treated.
Stroke is a 911 emergency. If recognized quickly, the experts at Pacific Stroke and Aneurysm Center can treat patients by offering blood clot-busting medication or a minimally invasive procedure to open a blocked artery that can minimize the effects of stroke. Providence Saint John’s Health Center is a Thrombectomy-Capable Stroke Center and Providence Little Company of Mary Medical Center Torrance is the first Comprehensive Stroke Center in the South Bay.
In addition to emergency care, we are committed to supporting the follow-up and recovery for stroke survivors at our clinic and support group. Pacific Neuroscience Institute also offers speech pathology for stroke patients.
Symptoms of a Stroke
The symptoms of a stroke can vary depending on the severity and location of the damage in the brain. Some common symptoms may include sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body; sudden confusion, trouble speaking, or difficulty understanding speech; sudden vision problems in one or both eyes; sudden dizziness, loss of balance, or difficulty walking; and a sudden, severe headache with no known cause.
Types of Stroke
There are three main types of stroke: ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, and a Transient Ischemic Attack. Ischemic stroke is the more common type and occurs when a blood clot blocks a blood vessel in the brain, while hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures and causes bleeding. A transient ischemic attack or “mini” stroke is caused by a temporary brain clot that stops or reduces blood flow to the brain.
Ischemic stroke
Caused by a clot obstructing the flow of blood to the brain
Hemorrhagic stroke
Caused when a blood vessel ruptures preventing blood flow to the brain
Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
Also called a “mini stroke”, TIA is caused by a temporary clot that reduces or stops blood flow to the brain
In the United States, approximately 800,000 people will suffer a stroke annually and it is the fifth leading cause of death in the U.S., behind heart disease, cancer, chronic lung disease, and accidents. More importantly, stroke is the leading cause of long-term adult disability in the U.S. Most people survive their first stroke, but their life and the lives of their family are forever changed.
Things to Know
- Stroke is largely preventable
- The sooner a stroke is recognized and treated, the less likely it will cause permanent disability
How to Identify a Stroke
Awareness is key in recognizing stroke symptoms. This is currently where we have the most work to do regarding stroke. For instance, did you know that two times more women die each year from stroke than from breast cancer? Despite this fact, a study done by the American Heart Association found that of women over age 25, only 25% could recognize signs of a stroke.
Stroke is time sensitive

Time lost equals brain lost. The typical patient loses about 2 million neurons per minute in which stroke is left untreated. Recognizing and reacting to the signs of stroke lead to significantly better outcomes, shorter hospital stays, and lower medical expenses. Acting quickly, in many cases, can stop stroke in its tracks and limit long-term disability.
Contact Us
The Pacific Stroke and Neurovascular Center’s state-of-the-art facilities are located at:
Providence Saint John’s Health Center
2125 Arizona Ave., Santa Monica, CA 90404
310-829-8319
Providence Little Company of Mary Medical Center Torrance
4201 Torrance Blvd., Suite 520, Torrance, CA 90503
424-212-5340
Providence Saint Joseph Medical Center
501 S. Buena Vista Ave., Burbank, CA 90505
818-847-6049
Providence Holy Cross Medical Center
15031 Rinaldi St, Mission Hills, CA 91345
818-847-6570